 / 01. PROTECT AGAINST THIRD-PARTY APP STORES.
/ 01. PROTECT AGAINST THIRD-PARTY APP STORES.
Don’t compromise on the endpoints you choose for your organization.
In a significant move,
Microsoft mandated that all its China-based employees switch from Android devices to iPhones. The absence of Google Play Services in China makes Android devices particularly vulnerable.
The EU’s Digital Markets Act (DMA) is also leaving room for untrusted sources, allowing third-party app stores to be accessible on devices. North American organizations are making a strategic shift and viewing this opportunity to assess risks associated with third-party app stores and maintain a secure mobile environment.
/ 02. REALLY ENFORCE YOUR MOBILE DEVICE POLICIES
Enroll devices in a unified endpoint management (UEM) program to enforce security policies and monitor usage.
Some employees might resist but failure to enforce these policies can result in significant security breaches, data and financial loss. Effective enforcement ensures compliance, reduces vulnerabilities and protects the organization's sensitive information from potential threats.
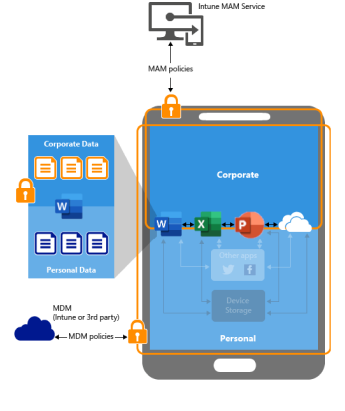
/ 03. IMPLEMENT DATA SECURITY MEASURES
UEM is effective for securing the device, enforcing policies, pushing applications and more.
However, many organizations stop there. They’re missing a critical step. Default UEM policies don’t protect your data, it’s when you use mobile application management (MAM) (E.g. InTune App Protection Policies) that your corporate data is protected, applications are limited, and your enterprise remains secure. Without implementing MAM policies organizations risk their data being stored on 3rd party cloud services and transmitted through non-secure mechanisms like iCloud, Google Drive and WhatsApp.
 / 04. EDUCATE AND EMPOWER YOUR EMPLOYEES
/ 04. EDUCATE AND EMPOWER YOUR EMPLOYEES
Your employees are your first line of defense and your biggest risk.
Regular training sessions can turn potential security risks into your strongest allies. Teach them to recognize threats and avoid risky behavior. After all, the smartest people can sometimes make the dumbest mistakes when they're not aware of the risks.
/ 05. SEPARATE CORPORATE AND PERSONAL DATA
Even with BYOD and company-issued devices, corporate and personal data must be kept separate.
Implement technology to create isolated environments for work-related data and applications. By maintaining strict boundaries, you minimize the risk of data breaches and compromise for both personal and corporate data.
/ 06. KEEP DEVICES UPDATED
Implement regular updates.
Regularly scheduled updates and ongoing patching ensures that devices have the latest protections against emerging threats and are protected against known vulnerabilities. Making it easier to automate updates and streamline the process for your team and ensure that no device is left vulnerable.
/ 07. USE STRONG AUTHENTICATION METHODS
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is the most basic but
the most important.

Remember: It’s harder for unauthorized users to gain access when they jump through multiple hoops. Implementing MFA reduces the risk of compromised credentials by adding layers of security. Regularly review and update authentication methods to stay ahead and encourage employees to use strong, unique passwords in conjunction with MFA.
/ 08. THINK GLOBAL
Companies must think beyond borders and adopt a holistic approach, considering regional variations and local threats.
Understanding regional nuances and integrating them into a global strategy is essential. Ensure your security measures are both globally unified and regionally adaptable, providing top-tier protection regardless of location.
/ TLDR
Mobile devices can be your greatest enterprise asset or your greatest security risk. Stay away from third-party app stores, enforce robust secuirty policies, seperate corporate and eprsonal data and keep your systems updates.